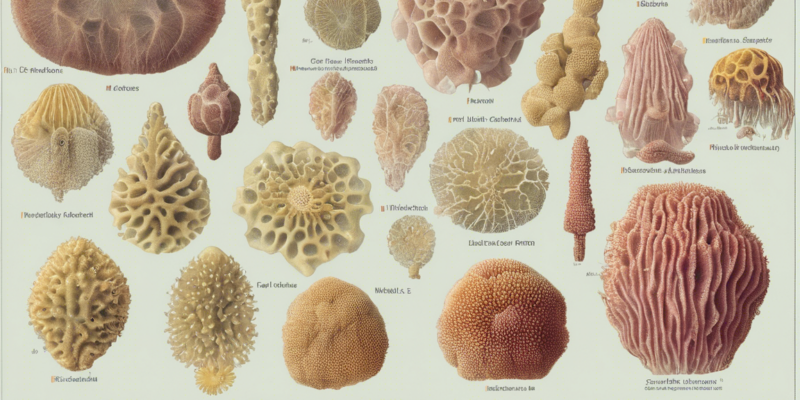
Porifera, commonly known as sponges, are fascinating and unique organisms that play a crucial role in marine ecosystems. Despite their seemingly simple appearance, sponges are incredibly diverse and exhibit a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors. In this article, we will delve into the world of Porifera taxonomy, exploring their classification and characteristics to gain a deeper understanding of these remarkable creatures.
Introduction to Porifera:
Porifera are multicellular, filter-feeding animals that are primarily marine but can also be found in freshwater environments. They are characterized by their lack of true tissues and organs, with most sponges being immobile as adults. Sponges are renowned for their ability to filter large volumes of water, extracting nutrients and oxygen while expelling waste products. This unique feeding strategy sets them apart from other members of the animal kingdom.
Classification of Porifera:
1. Class Calcarea (Calcispongiae):
– These sponges have a skeleton composed of calcium carbonate spicules. They are typically small in size and are found in shallow waters.
– Example: Leucosolenia
2. Class Hexactinellida (Glass sponges):
– Glass sponges have a siliceous skeleton made of six-rayed spicules fused together. They are often deep-sea inhabitants.
– Example: Euplectella
3. Class Demospongiae:
– Demosponges represent the largest and most diverse class of sponges, with a skeleton made of spongin fibers or siliceous spicules.
– Example: Spongilla
Characteristics of Porifera:
1. Body Structure:
– Sponges have a porous body with multiple channels and cavities through which water flows. These channels are lined with specialized cells called choanocytes, which generate a water current and capture food particles.
2. Reproduction:
– Sponges can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction usually involves the release of sperm and eggs into the water, where fertilization takes place externally. Asexual reproduction can occur through budding or the formation of gemmules.
3. Symmetry:
– Most sponges exhibit asymmetry or radial symmetry, although some species may display a degree of bilateral symmetry during certain stages of their lifecycle.
4. Spicules:
– Spicules are microscopic structures that provide structural support to the sponge’s body. These spicules can be composed of calcium carbonate, silica, or spongin, depending on the species.
5. Filter Feeding:
– Sponges are filter feeders that rely on the flow of water through their bodies to obtain food particles and oxygen. Choanocytes play a crucial role in capturing and engulfing food particles.
Ecology and Importance of Porifera:
Porifera play a vital role in marine ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling and providing habitat for a diverse array of organisms. Sponges filter large volumes of water, helping to maintain water clarity and quality. Additionally, some compounds isolated from sponges have shown potential pharmaceutical applications, highlighting their importance beyond ecological roles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Porifera:
Q1: Are all sponges marine organisms?
A: While the majority of sponges are marine, some species can also be found in freshwater habitats.
Q2: Do sponges have predators?
A: Yes, sponges are preyed upon by various organisms, including sea slugs, sea stars, and fish.
Q3: Can sponges move from one place to another?
A: Sponges are generally sessile as adults, meaning they are immobile and anchored to a substrate.
Q4: How do sponges reproduce asexually?
A: Sponges can reproduce asexually through budding, where a new individual grows as an outgrowth from the parent sponge.
Q5: Are all sponges filter feeders?
A: Yes, all sponges are filter feeders, relying on the flow of water to obtain nutrients and oxygen.
Q6: Can sponges regenerate if damaged?
A: Sponges have remarkable regenerative abilities and can often regenerate lost or damaged body parts.
Q7: What is the role of spicules in sponges?
A: Spicules provide structural support to the sponge’s body, helping maintain its shape and integrity.
Q8: Do sponges have nervous systems?
A: Sponges lack true nervous systems but have specialized cells that coordinate various physiological functions.
Q9: How long do sponges live?
A: The lifespan of sponges can vary depending on the species, with some living for decades or even centuries in favorable conditions.
Q10: Can sponges be harmful to humans?
A: While most sponges are harmless, some species can produce toxins that are harmful to humans if touched or ingested.
Conclusion:
Porifera, or sponges, are an intriguing group of animals with unique characteristics and ecological importance. By exploring their taxonomy, classification, and key features, we gain a deeper appreciation for these often-underappreciated organisms. Sponges serve as valuable indicators of ecosystem health and biodiversity, underscoring the need for their conservation and protection in marine environments.












Comments